
If you’re searching for a cost-effective, durable piping solution, understanding the ERW pipe definition is crucial. ERW (Electric Resistance Welded) pipes are widely used in construction, oil and gas, and water supply systems due to their efficiency and affordability. This article explains what ERW pipes are, how they’re made, their key applications, and industry standards.
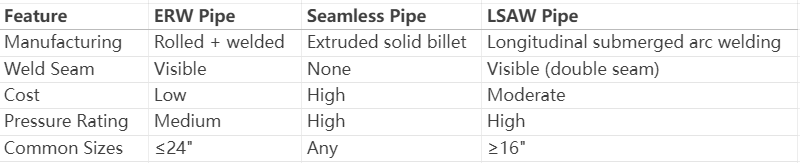
ERW pipe definition: An Electric Resistance Welded (ERW) pipe is a type of steel pipe manufactured by rolling metal sheets and welding the edges using high-frequency electrical current. Unlike seamless pipes, ERW pipes have a visible weld seam but offer excellent strength-to-cost ratios for low-to-medium pressure applications.
· Material: Typically made from carbon steel (e.g., ASTM A53, API 5L).
· Welding Method: High-frequency induction or contact welding.
· Sizes: Common diameters range from ½ inch to 24 inches.
· Surface Finish: Can be galvanized, black, or coated for corrosion resistance.
The production of ERW pipes involves these key steps:
· Hot-rolled or cold-rolled steel coils are slit into required widths.
· The flat strip is fed through forming rollers that bend it into a cylindrical shape.
· The open edges are heated using an electric current (skin effect) and pressed together to form a solid weld without filler material.
· The welded pipe passes through sizing rolls to achieve precise dimensions before being cut to length.
· ERW pipes undergo non-destructive testing (NDT) like ultrasonic (UT) or hydrostatic tests to ensure weld integrity.
Why Choose ERW Pipes?
· Economical: Lower production cost than seamless pipes.
· Efficient: Faster manufacturing for large-scale projects.
· Versatile: Suitable for water, gas, and structural uses.
Due to their balance of strength and affordability, ERW pipes are used in:
· Oil & Gas: Transporting non-corrosive fluids.
· Water Supply: Municipal and industrial plumbing.
· Construction: Scaffolding, fencing, and structural frameworks.
· Automotive: Exhaust systems and chassis components.
To ensure quality, ERW pipes comply with international standards such as:
· API 5L: For petroleum and natural gas industries.
· ASTM A53: General-purpose carbon steel pipes.
· EN 10219: European standard for welded structural pipes.
ERW pipes are ideal for low-to-medium pressure systems. For extreme pressures (e.g., deep-sea pipelines), seamless or LSAW pipes are preferred.
Yes, but coatings (galvanization, epoxy) significantly improve corrosion resistance.
HFW (High-Frequency Welded) is a subtype of ERW with a more precise, automated welding process.
Understanding the ERW pipe definition helps industries select the right piping solution. ERW pipes offer a cost-effective, reliable option for fluid transport and structural needs, backed by standardized manufacturing processes. Whether for plumbing, construction, or energy projects, ERW pipes remain a top choice for balanced performance and affordability.
Looking for high-quality ERW pipes? Get in touch—we supply ASTM, API, and EN-compliant pipes tailored to your project needs.