
High-Frequency Welded (HFW) steel pipe is widely used in oil and gas transportation, structural applications, and mechanical tubing. Because its performance directly affects the safety and reliability of critical projects, understanding international standards is essential for engineers, manufacturers, and buyers. This article explains how the API, ASTM, and EN standards regulate the quality, dimensions, and testing requirements for HFW steel pipe, providing a clear technical reference for global users.
HFW (High-Frequency Welding) is a specialized electric resistance welding process. It uses high-frequency current to heat the edges of a steel strip, which are then pressed together to form a longitudinal weld. The process ensures strong, uniform joints with minimal heat-affected zones compared to conventional ERW (Electric Resistance Welding).
Typical advantages of HFW steel pipe include:
· High production efficiency
· Precise dimensional control
· Excellent weld integrity and mechanical strength
· Suitability for pipelines and structural applications
Because HFW pipes are produced in large quantities and used across multiple industries, compliance with recognized standards like API, ASTM, and EN is vital.
The American Petroleum Institute (API) sets global standards for steel pipes used in the transportation of oil, gas, and water. The most relevant specification is API 5L, which covers seamless and welded pipes, including HFW.
Key points in API 5L for HFW steel pipe:
· Grades: PSL1 and PSL2 categories, with grades ranging from B to X80.
· Welding type: HFW is listed as an acceptable manufacturing process for welded line pipe.
· Mechanical properties: Yield strength, tensile strength, and elongation requirements depend on grade and wall thickness.
· Non-Destructive Testing (NDT): 100% ultrasonic testing of the weld seam is mandatory for HFW pipes.
· Dimensional tolerances: Governed by OD (outside diameter), wall thickness, and roundness criteria.
In practice, HFW steel pipes meeting API 5L PSL2 are commonly used in high-pressure pipeline projects due to their strict mechanical and chemical property requirements.
The American Society for Testing and Materials (ASTM) publishes several standards relevant to HFW production, each tailored to specific applications:
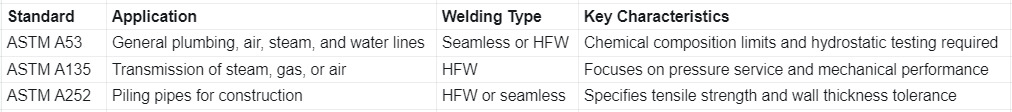
Under ASTM A53, HFW pipes are categorized as Type E (Electric-Resistance Welded) and must undergo NDT, flattening tests, and hydrostatic tests to ensure weld soundness.
These ASTM standards ensure that HFW steel pipe can safely handle various service conditions, from high-pressure fluid transport to structural support.
European standards (EN) define precise requirements for welded steel pipes used in pressure and structural systems.
· EN 10217 – Welded steel tubes for pressure purposes
o Part 2 (EN 10217-2): Covers electric welded non-alloy and alloy steel tubes with specified elevated-temperature properties.
o Requires NDT and weld seam heat treatment to reduce residual stress in HFW pipes.
· EN 10219 – Cold-formed welded structural hollow sections of non-alloy and fine-grain steels
o Specifies dimensional tolerances, impact testing, and yield strength requirements.
o Widely applied in construction, mechanical, and offshore structures.
HFW pipes produced under EN 10217-2 or EN 10219-1 must undergo visual inspection, ultrasonic testing, and dimensional verification to guarantee compliance with European quality benchmarks.
To meet API, ASTM, or EN standards, every HFW steel pipe must pass stringent quality control and inspection steps, including:
· Visual and Dimensional Inspection (OD, WT, straightness, end finish)
· Hydrostatic Testing to confirm pressure resistance
· Ultrasonic or Eddy-Current Testing for weld seam integrity
· Mechanical Testing (tensile, bend, flattening tests)
· Chemical Analysis to ensure consistent material composition
These tests confirm that the weld seam and pipe body meet the same performance criteria, ensuring the reliability of pipelines and structural systems.
Selecting the correct standard depends on the pipe’s end-use:

Compliance with these standards not only ensures safety and reliability but also facilitates international trade by providing a consistent technical framework.
Understanding international standards for HFW steel pipes is crucial for anyone involved in design, procurement, or manufacturing.
Whether following API 5L, ASTM A53, or EN 10217, each specification defines strict guidelines for materials, welding processes, mechanical performance, and testing procedures.
By ensuring compliance with these standards, manufacturers can deliver HFW steel pipe products that meet global quality expectations, while engineers and buyers can confidently specify materials that ensure long-term performance and safety.